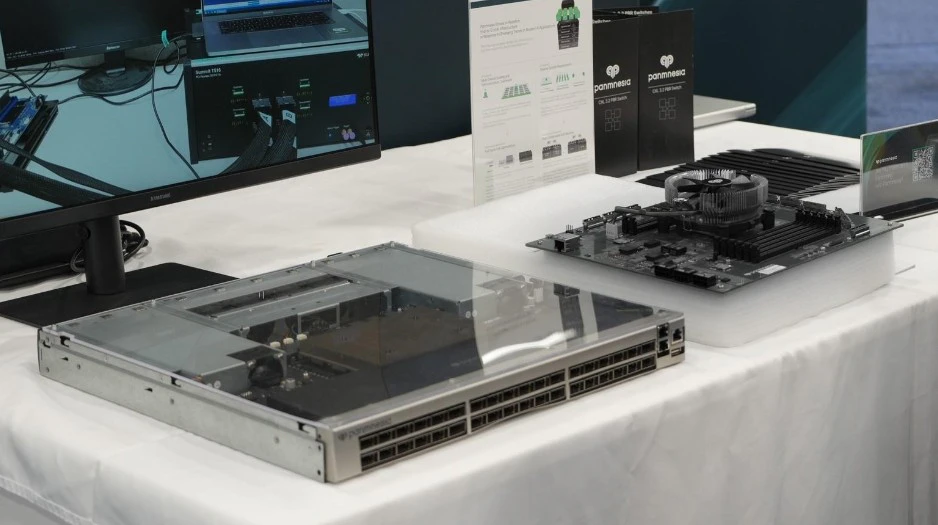
Panmnesia Showcases CXL Switch-Based High-Performance Computing Solution at ISC High Performance 2025
Share
Panmnesia, a company specializing in link solutions for AI infrastructure, participated in ISC High Performance 2025 (International Supercomputing Conference High Performance 2025), held in Hamburg, Germany, from June 10 to 12. At the event, the company unveiled a end-to-end high-performance computing (HPC) solution based on servers equipped with its CXL 3.x Switches.

About ISC High Performance 2025
As the largest HPC exhibition in Europe and one of the most prominent global events in the field—alongside SC—ISC 2025 marked its 40th anniversary this year. More than 3,000 professionals gathered to discuss the latest developments in HPC hardware, management software, and AI acceleration technologies.

Panmnesia's Exhibit: CXL 3.x Switch-Based HPC Solution
Making its debut at ISC, Panmnesia introduced a framework incorporating its flagship technologies: a end-to-end HPC server solution featuring its CXL 3.x Switches and CXL 3.x Intellectual Property (IP). This integrated hardware-software system enables flexible resource scaling and enhances parallel computing performance through CXL-based memory sharing.
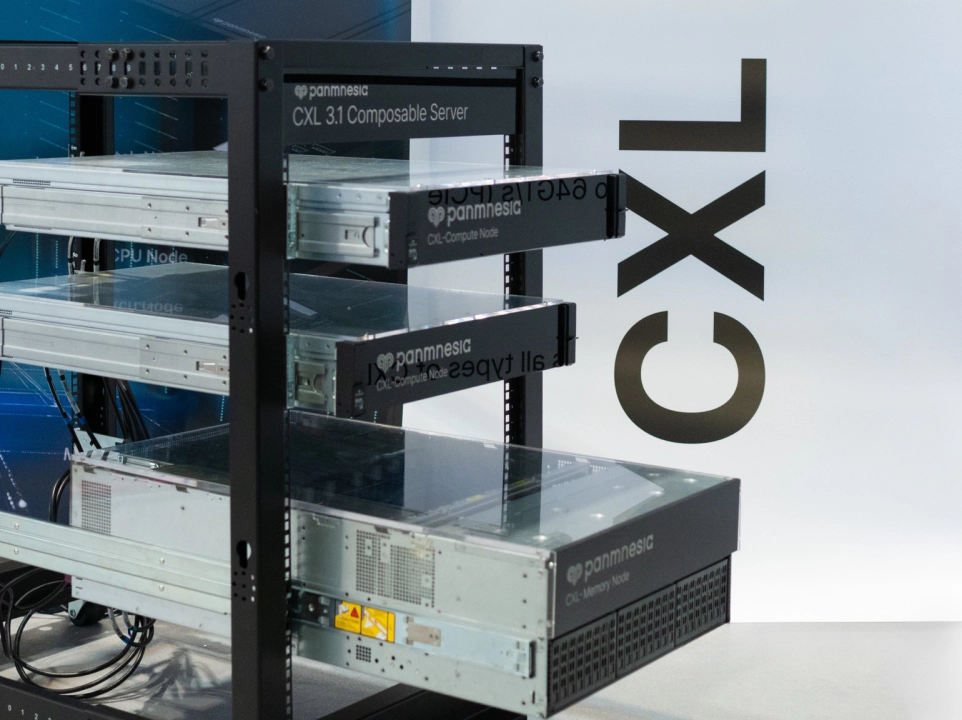

Hardware Stack: Cost-Optimized Composable Server Architecture
Panmnesia’s hardware stack addresses the cost-efficiency limitations of conventional HPC systems. Traditionally, HPC servers are provisioned with fixed ratios of compute and memory resources. Therefore, when more memory capacity is required, users are often forced to add entire servers—along with redundant compute resources—resulting in inflated costs.
In contrast, Panmnesia's composable architecture enables independent scaling of compute and memory resources. The CXL 3.x Composable Server exhibited at ISC consists of separate compute nodes (featuring CXL-enabled CPUs or GPUs) and memory nodes (featuring CXL-enabled memory expanders), all interconnected via CXL Switches. This configuration allows users to selectively add only the nodes equipped with the resources they need, thereby reducing unnecessary expenditure (Figure 3). For example, when memory capacity is insufficient, users can add only memory nodes—without additional compute resources—to meet the required memory demand.
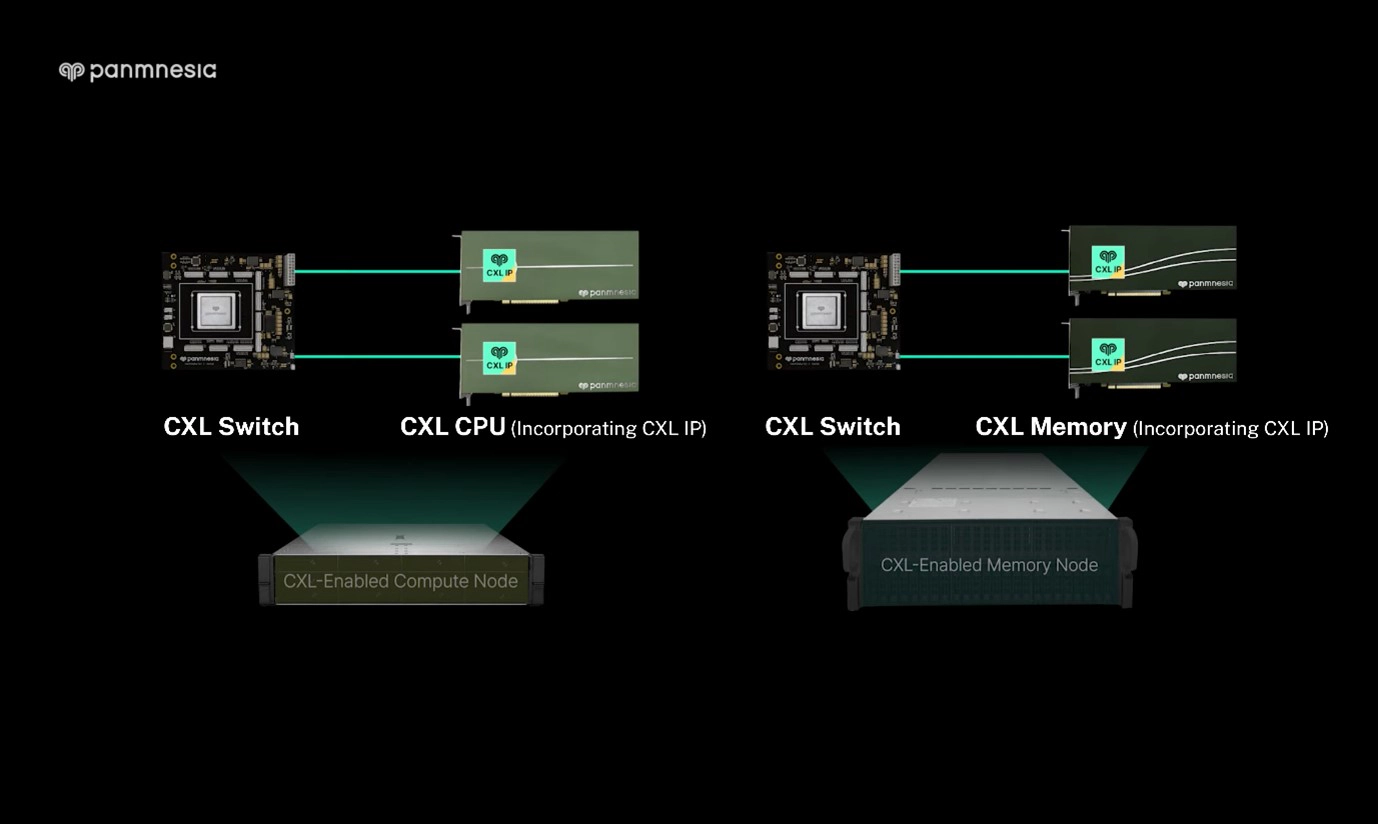
At the core of this architecture are Panmnesia’s two main products: the CXL Switch and CXL IP. First, Panmnesia’s CXL Switch connects multiple nodes, making it possible to build a unified system. In particular, Panmnesia’s CXL Switch stands out in that it supports flexible configurations in terms of device types, system scale, and connection topology. It interconnects not only CPUs and memory, but also GPUs (graphics processing units), NPUs (neural processing units), and various other accelerators. It further enables scalability to multiple server nodes/racks by supporting advanced features of the latest CXL standards, such as multi-level switching and port-based routing.
Panmnesia’s CXL IP enables seamless memory sharing and access across these interconnected devices. As Panmnesia’s low-latency IP which achieved the world’s first double-digit nanosecond latency autonomously performs memory management operations, it can minimize the performance overhead.
Software Stack: Accelerating Parallel Computing
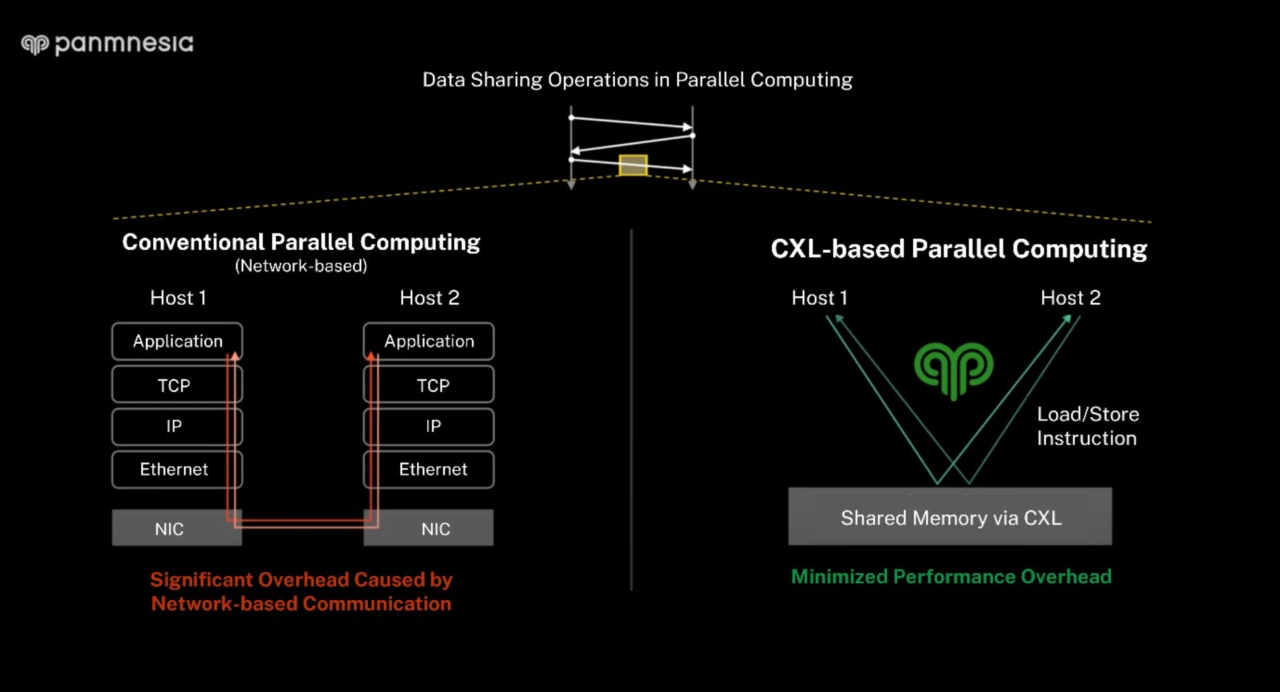
Complementing its hardware, Panmnesia also introduced a software stack designed to accelerate parallel computing applications. In traditional HPC systems, data is distributed across the memory attached to each server node, requiring frequent inter-node communication. This often leads to performance degradation due to redundant data copying and format transformation.
Panmnesia’s approach addresses these inefficiencies by replacing network-based communication with CXL-based memory sharing. Instead of distributing data across the local memory of individual server nodes, it is stored in a unified memory pool—composed of multiple memory nodes—that is accessible by all compute nodes via CXL. With Panmnesia's low-latency CXL IP autonomously handling memory management operations, processing units (e.g., CPUs, GPUs) can access the shared memory using standard load/store instructions. This significantly reduces the latency and overhead typically caused by data copying and transformation during network-based communication.
Panmnesia implemented this software stack on a Linux-based system and directly executed a fluid dynamics simulation—a representative parallel computing workload—to demonstrate its effectiveness. The demonstration resulted in a 44% reduction in execution time.

A Panmnesia spokesperson stated, “Many server-related companies visited our booth and expressed strong interest in our CXL Switch chip and solution. It was a valuable opportunity to introduce our technology and products to potential customers in Europe and to explore future collaboration.”
Meanwhile, more information on Panmnesia’s products and demonstration videos is available on the company’s official YouTube channel and LinkedIn page.